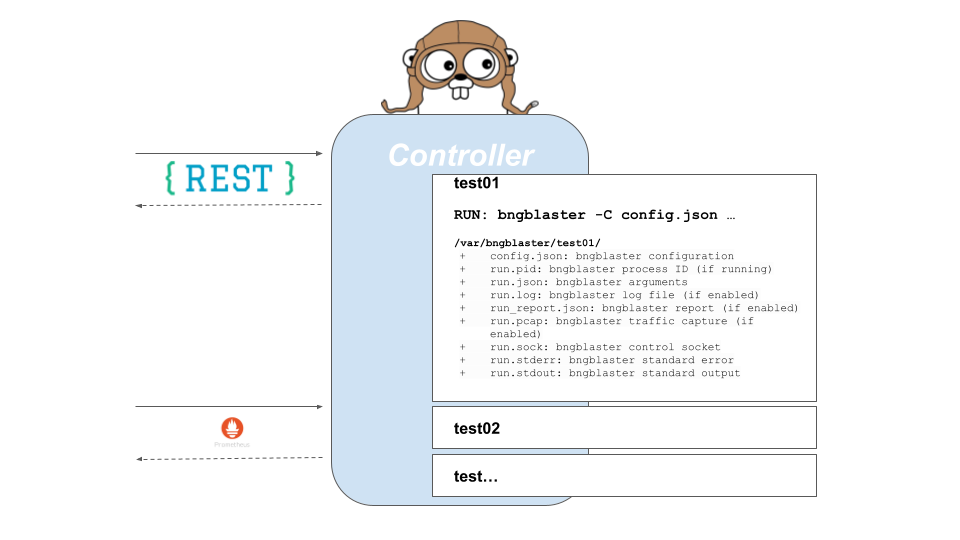
Controller
The BNG Blaster controller offers a convenient REST API that allows users to start and stop multiple test instances with ease. The REST API serves as an interface to the BNG Blaster’s underlying functionality, providing a simplified way to interact with the controller and manage test instances.
By exposing the BNG Blaster JSON RPC API as a REST API, the controller enables users to perform various operations programmatically. This includes initiating test instances, configuring test parameters, monitoring test progress, and terminating test executions. The REST API provides a standardized and intuitive way to control the BNG Blaster, making it accessible to automation scripts, external applications, or custom integrations.
Furthermore, the BNG Blaster controller’s REST API also offers endpoints to download logs and reports. These endpoints enable users to retrieve detailed information about the test execution, such as test results, performance metrics, and any encountered errors or issues. By accessing logs and reports through the REST API, users can analyze the outcomes of their tests, troubleshoot problems, and generate comprehensive documentation for further analysis or reporting purposes.
The REST API provided by the BNG Blaster controller simplifies the management of test instances and enhances the overall usability and integration capabilities of the BNG Blaster. Whether it’s starting and stopping tests, retrieving logs and reports, or integrating with other systems, the REST API streamlines the testing process and facilitates seamless interaction with the BNG Blaster’s functionalities.
https://github.com/rtbrick/bngblaster-controller
Installation
The BNG Blaster controller should run on any modern Linux distribution but is primarily tested on Debian Bookworm and Ubuntu 22.04 LTS.
Download and install Debian package: https://github.com/rtbrick/bngblaster-controller/releases
$ wget https://github.com/rtbrick/bngblaster-controller/releases/download/<version>/bngblaster-controller_<version>_amd64.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i bngblaster-controller_<version>_amd64.deb
The corresponding service will be started automatically.
$ systemctl status rtbrick-bngblasterctrl.service
● rtbrick-bngblasterctrl.service - RtBrick BNG Blaster Controller
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rtbrick-bngblasterctrl.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2022-07-01 11:14:01 UTC; 7min ago
Main PID: 682535 (bngblasterctrl)
Tasks: 8 (limit: 309235)
Memory: 2.6M
CGroup: /system.slice/rtbrick-bngblasterctrl.service
└─682535 /usr/local/bin/bngblasterctrl
The BNG Blaster controller listens on port 8001 per default, which can be changed using the argument -addr in the systemd service unit /etc/systemd/system/bngblaster-controller.service.
$ sudo bngblasterctrl --help
Usage of bngblasterctrl:
-addr string
HTTP network address (default ":8001")
-color
turn on color of color output
-console
turn on pretty console logging (default true)
-d string
config folder (default "/var/bngblaster")
-debug
turn on debug logging
-e string
bngblaster executable (default "/usr/sbin/bngblaster")
API
OpenAPI: https://rtbrick.github.io/bngblaster-controller/
Create Test Instance
PUT /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>
This API endpoint creates a test instance if not already created. The body of this request is stored as bngblaster configuration (config.json).
Each test instance creates a directory in /var/bngblaster/<instance-name>. This directory contains the following files:
config.json: bngblaster configuration
run.pid: bngblaster process ID (if running)
run.json: bngblaster arguments
run.log: bngblaster log file (if enabled)
run_report.json: bngblaster report (if enabled)
run.pcap: bngblaster traffic capture (if enabled)
run.sock: bngblaster control socket
run.stderr: bngblaster standard error
run.stdout: bngblaster standard output
Example:
curl --location --request PUT 'http://10.10.10.10:8001/api/v1/instances/quickstart_pppoe' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"interfaces": {
"a10nsp": [
{
"__comment__": "PPPoE Server",
"interface": "veth1.1"
}
],
"access": [
{
"__comment__": "PPPoE Client",
"interface": "veth1.2",
"type": "pppoe",
"outer-vlan-min": 1,
"outer-vlan-max": 4000,
"inner-vlan": 7
}
]
}
}'
Start Test
POST /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/_start
The start API endpoint will start the bngblaster with the argument options defined in the body.
{
"logging": true,
"logging_flags": [
"debug",
"ip"
],
"report": true,
"session_count": 1000
}
All supported argument options are explained in the OpenAPI schema.
Example:
curl --location --request POST 'http://10.10.10.10:8001/api/v1/instances/quickstart_pppoe/_start' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"logging": true,
"logging_flags": [
"debug",
"pppoe",
"ip"
],
"report": true,
"session_count": 2
}'
Status
GET /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>
The status API endpoint returns the status of the test which can be either started or stopped.
Command
POST /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/_command
The JSON body of this API call will be passed to the bngblaster instance control socket (/var/bngbnlaster/<instance-name>/run.sock). The result will be passed back to the client.
Example:
curl --location --request POST 'http://10.10.10.10:8001/api/v1/instances/quickstart_pppoe/_command' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"command": "session-info",
"arguments": {
"session-id": 1
}
}'
{
"status": "ok",
"code": 200,
"session-info": {
"type": "pppoe",
"session-id": 1,
"session-state": "Established",
"...": "..."
}
}
The result code is passed as HTTP response status code.
{
"status": "warning",
"code": 404,
"message": "session not found"
}
Stop Test
POST /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/_stop
The stop API endpoint will send the SIGINT signal to the corresponding BNG blaster instance (kill -INT <pid>).
Delete Test Instance
DELETE /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>
This API endpoint deletes the test instance directory. The corresponding test run is forcefully terminated (kill -9 <pid>) if running.
Reports
The BNG Blaster can generate detailed reports at the end of the test execution. Those reports must be enabled during the start with the argument option report. This detailed report can be further enhanced using report_flags to include detailed per-session and stream results. Consider that the resulting report may be large if streams flag is enabled in combination with a huge amount of streams (around 500MB report file for one million streams).
POST /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/_start
{ "report": true, "report_flags": [ "sessions", "streams" ] }
The final report can be retrieved with the following request after the test has finally stopped.
GET /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/run_report.json
After requesting the test to stop, it can take some time until the test has gracefully stopped. This can be verified using the status command. As soon as the status becomes stopped, the report file should be available.
Logs
The BNG Blaster supports extensive logging during the test execution. This log file must be enabled during the start with the argument option logging. The optional argument logging_flags allows for enabling log categories.
POST /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/_start
{ "logging": true, "logging_flags": [ "bgp", "isis", "ip" ] }
Please check logging section for detailed list of all logging flags.
The final log file can be retrieved with the following request after the test has finally stopped.
GET /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/run.log
It is also possible to retrieve the standard output and error for troubleshooting purposes.
GET /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/run.stderr GET /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/run.stdout
PCAP
The BNG Blaster supports to capture all traffic sent and received by the BNG Blaster which must be enabled during the start with the argument option pcap_capture.
POST /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/_start
{ "pcap_capture": true }
The final capture file can be retrieved with the following request after the test has finally stopped.
GET /api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/run.pcap
Metrics
GET /metrics
This endpoint returns metrics for all instances in Prometheus text format.
# HELP instances_running The number of running instances
# TYPE instances_running gauge
instances_running{hostname="blaster"} 0
# HELP instances_total The total number of instances
# TYPE instances_total gauge
instances_total{hostname="blaster"} 4
The metric instances_total counts the number of test instance directories present and instances_running shows how many of them are running.
Every metric is labeled with the hostname where the controller is running.
Per default, there are no metrics per instance. This has to be explicitly enabled during instance start (/api/v1/instances/<instance-name>/_start) using the new metric_flags option.
{
"logging": true,
"logging_flags": [
"error",
"ip"
],
"metric_flags": [
"session_counters",
"interfaces"
]
}
Currently, the following metrics are supported:
session_counters session statistics
interfaces interface/link counters
access_interfaces access interface function counters
network_interfaces network interface function counters
a10nsp_interfaces a10nsp interface function counters
streams stream counters
The streams metric generates statistics for every stream and direction. Therefore the streams metric should not be used with massive streams (e.g. > 10.000 streams) but there is no limit enforced.
# HELP sessions The total number of sessions
# TYPE sessions counter
sessions{hostname="blaster",instance_name="test"} 10
# HELP sessions_established The number of sessions in the state established
# TYPE sessions_established gauge
sessions_established{hostname="blaster",instance_name="test"} 10
...
Instance metrics are labeled with the instance name. All interface-specific metrics are also labeled with the corresponding interface name and type.
# HELP interfaces_rx_packets Interface RX packets
# TYPE interfaces_rx_packets counter
interfaces_rx_packets{hostname="rbfs",instance_name="test",interface_name="eth1",interface_type="Interface"} 163
interfaces_rx_packets{hostname="rbfs",instance_name="test",interface_name="eth11",interface_type="Network"} 155
interfaces_rx_packets{hostname="rbfs",instance_name="test",interface_name="eth12",interface_type="Interface"} 158
interfaces_rx_packets{hostname="rbfs",instance_name="test",interface_name="eth12",interface_type="Access"} 150
...