Interfaces
The BNG Blaster distinguishes between interface links and interface functions. An interface link can be considered as the actual interface with all the corresponding IO settings. This is similar but not the same as physical interfaces in typical router implementations. Interface functions are similar to logical interfaces and define the actual services. One or more interface functions can be attached to each interface link.
At least one interface function is required to start the BNG Blaster.
Operating System Settings
The BNG Blaster implements all protocols in user space. Therefore the used interfaces links must not have an IP address configured in the host operating system, to prevent that the received packets are handled or even responded to from the Linux kernel as well.
All used interface links must be in an operational state up.
sudo ip link set dev <interface> up
It is not possible to send packets larger than the configured interface MTU, which is 1500 bytes per default. For PPPoE with multiple VLAN headers, this might be not enough for large packets. Therefore the interface MTU should be increased using the following commands.
sudo ip link set mtu 9000 dev <interface>
All this can be also archived via netplan using the following configuration for each BNG Blaster interface link.
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
eth1:
dhcp4: no
dhcp6: no
link-local: []
mtu: 9000
eth2:
dhcp4: no
dhcp6: no
link-local: []
mtu: 9000
It might be also needed to increase the hardware and software queue size of your network interface links for higher throughput.
The command ethtool -g <interface> shows the currently applied and maximum
hardware queue size.
$ sudo ethtool -g ens5f1
Ring parameters for ens5f1:
Pre-set maximums:
RX: 4096
RX Mini: 0
RX Jumbo: 0
TX: 4096
Current hardware settings:
RX: 512
RX Mini: 0
RX Jumbo: 0
TX: 512
The currently applied settings can be changed with the following command:
sudo ethtool -G ens5f1 tx 4096 rx 4096
You can even change the software queue size:
sudo ip link set txqueuelen 4096 dev ens5f1
Interface Settings
The interfaces section contains all configurations around interface links and options.
{ "interfaces": {} }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
io-mode |
IO mode.
The supported IO modes are listed with
bngblaster -vbut except
packet_mmap_raw all other modes are currentlyconsidered experimental. In the default mode (
packet_mmap_raw)all packets are received in a Packet MMAP ring buffer and sent
directly through RAW packet sockets.
Default: packet_mmap_raw
|
io-slots |
IO slots (ring size).
It might be also needed to increase the io-slots to
reach the desired throughput. The actual meaning of IO slots
depends on the selected IO mode. For Packet MMAP, it defines the
maximum number of packets in the ring buffer.
Default: 4096
|
io-burst |
IO burst (packets).
Default: 256 Range: 1 to 65535
|
qdisc-bypass |
Bypass the kernel’s qdisc layer.
It’s currently not recommended to change the default (issue #206)!
Default: true
|
tx-interval |
TX polling interval in milliseconds.
Default: 0.1 Range: 0.0001 to 1000
|
rx-interval |
RX polling interval in milliseconds.
Default: 0.1 Range: 0.0001 to 1000
|
tx-threads |
Number of TX threads per interface link.
Default: 0 (main thread)
|
rx-threads |
Number of RX threads per interface link.
Default: 0 (main thread)
|
capture-include-streams |
Include traffic streams in the capture.
Default: false
|
mac-modifier |
Third byte of access session MAC address (0-255). This option
allows to run multiple BNG Blaster instances with disjoint session
MAC addresses.
Default: 0
|
{
"interfaces": {
"tx-interval": 0.1,
"rx-interval": 0.1,
"io-slots": 4096,
}
}
Links
The link configuration is optional and allows to define per interface link configurations. An explicit link configuration with the global default settings is automatically generated if no link is defined for interface links referenced by interface functions.
The link configuration is optional and allows to define per interface link configurations. An explicit link configuration with the global default settings is automatically generated if no link is defined for interface links referenced by interface functions.
{ "interfaces": { "links": [] } }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
interface |
Interface name (e.g. eth0, …).
|
description |
Interface description.
|
mac |
Overwrite the MAC address.
Default: physical interface MAC address
|
lag-interface |
Add interface/link to LAG group.
|
lacp-priority |
LACP interface priority.
Default: 32768
|
tx-cpuset |
Optionally pin TX threads to CPU cores (cpuset). This is required
for DPDK only.
|
rx-cpuset |
Optionally pin RX threads to CPU cores (cpuset). This is required
for DPDK only.
|
io-mode |
Overwrite the IO mode.
|
io-burst |
Overwrite the IO burst.
|
io-slots |
Overwrite the IO slots (ring size).
|
io-slots-tx |
Overwrite the TX IO slots (ring size).
|
io-slots-rx |
Overwrite the RX IO slots (ring size).
|
qdisc-bypass |
Overwrite the kernel’s qdisc layer configuration.
|
tx-interval |
Overwrite the TX polling interval in milliseconds.
|
rx-interval |
Overwrite the RX polling interval in milliseconds.
|
tx-threads |
Overwrite the number of TX threads per interface link.
|
rx-threads |
Overwrite the number of RX threads per interface link.
|
{
"interfaces": {
"tx-interval": 0.1,
"rx-interval": 0.1,
"io-slots": 4096,
}
}
Link Aggregation (LAG)
The BNG Blaster supports link aggregation (LAG) with and without LACP. The created LAG interface can be used as the parent interface link for all kinds of interface functions.
{ "interfaces": { "lag": [] } }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
interface |
LAG interface name (e.g. lag0, …).
|
lacp |
Enable LACP.
Default: false
|
lacp-timeout-short |
Enable LACP short timeout (3x1s)
Default: false (3x30s)
|
lacp-system-priority |
LACP system priority.
Default: 32768
|
lacp-system-id |
LACP system identifier
Default: 02:ff:ff:ff:ff:00
|
lacp-min-active-links |
Define the minimum number of active links.
Default: 0
|
lacp-max-active-links |
Limit the maximum number of active links.
Default: 255
|
mac |
LAG interface MAC address.
Default: 02:ff:ff:ff:ff:<interface-id>
|
Note
Multithreaded TX is not supported for LAG member interfaces!
{
"interfaces": {
"lag": [
{
"interface": "lag1",
"lacp": true,
"lacp-timeout-short": true
}
],
"links": [
{
"interface": "eth1",
"lag-interface": "lag1"
},
{
"interface": "eth1",
"lag-interface": "lag1"
}
],
"network": [
{
"interface": "lag1",
"address": "10.100.0.2/24",
"gateway": "10.100.0.1"
}
]
}
}
Interface Functions
The BNG Blaster supports three types of interface functions,
network, access, and a10nsp.
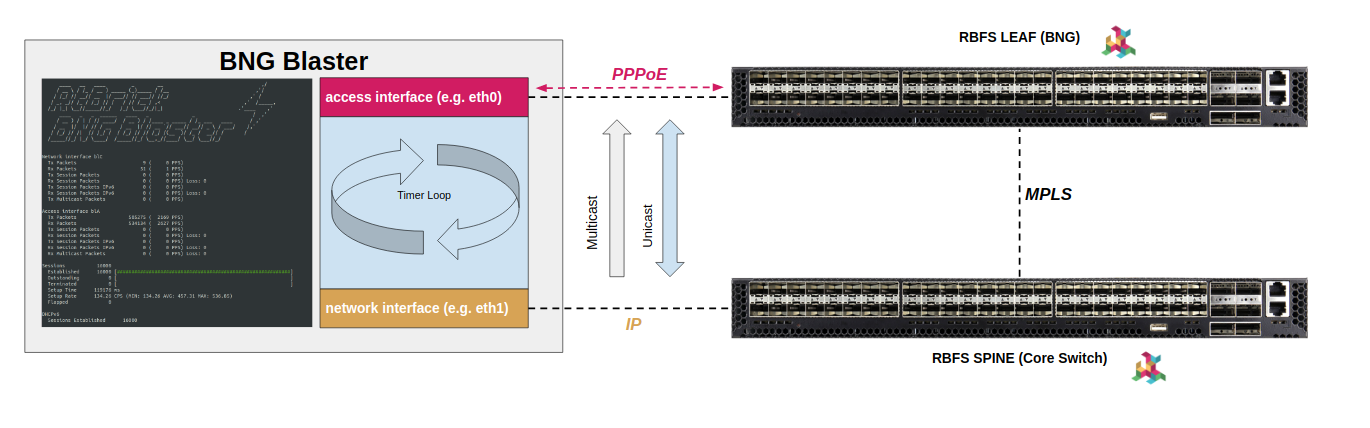
Network Interfaces
The network interfaces are used to emulate the core-facing side of the internet with optional routing protocols and traffic.
Those interfaces can communicate with the configured gateway only. Meaning that all traffic sent from the network interface will be sent to the learned MAC address of the configured gateway.
The network interface behaves like a router. It accepts all traffic sent to its own MAC address. This allows sending and receiving traffic for prefixes advertised via routing protocols or configured via static routes on the connected device under test.
The network interfaces are also used to inject downstream multicast test traffic for IPTV tests. It is also possible to send RAW traffic streams between network interfaces without any access interface defined for non-BNG testing.
The BNG Blaster responds to all ICMP echo requests sent to its own MAC address.
{ "interfaces": { "network": [] } }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
interface |
Parent interface/link name (e.g. eth0, …).
|
address |
Local IPv4 address (e.g. 10.0.0.1/24).
|
gateway |
Default gateway IPv4 address.
|
address-ipv6 |
Local IPv6 address (e.g. fc66::1/64).
|
gateway-ipv6 |
Default gateway IPv6 address.
|
ipv6-router-advertisement |
Send IPv6 router advertisements (ICMPv6 RA).
Default: true
|
mtu |
MTU size.
Default: 1500 Range: 64 - 9000
|
vlan |
Network interface VLAN.
Default: 0 (untagged)
|
gateway-mac |
Optional set default gateway MAC address manually. Per default
this MAC address is resolved via ARP/ND.
|
gateway-resolve-wait |
Sessions and protocols will not start until gateways are resolved.
Default: true
|
isis-instance-id |
Assign the interface to an ISIS instance.
|
isis-level |
ISIS interface level.
Default: 3 Range: 1 - 3
|
isis-p2p |
ISIS P2P interface.
Default: true
|
isis-l1-metric |
ISIS level 1 interface metric.
Default: 10
|
isis-l2-metric |
ISIS level 2 interface metric.
Default: 10
|
isis-l1-priority |
ISIS level 1 interface priority.
Default: 10
|
isis-l2-priority |
ISIS level 2 interface priority.
Default: 10
|
ospfv2-instance-id |
Assign the interface to an OSPFv2 instance.
|
ospfv2-type |
OSPFv2 interface type (p2p or broadcast).
Default: broadcast
|
ospfv2-metric |
OSPFv2 interface metric.
Default: 10
|
ospfv3-instance-id |
Assign the interface to an OSPFv3 instance.
|
ospfv3-type |
OSPFv3 interface type (p2p or broadcast).
Default: broadcast
|
ospfv3-metric |
OSPFv3 interface metric.
Default: 10
|
ldp-instance-id |
Assign the interface to a LDP instance.
|
cfm-cc |
Enable EOAM CFM CC.
Default: false
|
cfm-level |
Set EOAM CFM maintenance domain level.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 7
|
cfm-interval |
Set EOAM CFM CCM interval (IEEE 802.1Q encoding).
Values: 3.33ms, 10ms, 100ms, 1s, 10s, 1min, 10min
Default: 1s
|
cfm-md-name |
Set EOAM CFM maintenance domain name (string).
|
cfm-md-name-format |
Set EOAM CFM MD name format.
Default:
NONEValues:
NONE (1) NONEDNS (2) STRINGMAC_INT (3) aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff/123STRING (4) STRING |
cfm-ma-id |
Set EOAM CFM maintenance association identifier.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 65535
|
cfm-ma-name |
Set EOAM CFM maintenance association short name (string).
|
cfm-ma-name-format |
Set EOAM CFM MA name format.
Default:
STRINGValues:
VLAN (1) VLANSTRING (2) STRINGUINT16 (3) NumberVPN_ID (4) 14 hex digitsICC (32) 13 ASCII chars |
cfm-seq |
Enable EOAM CFM CC sequence numbers.
Default: true
|
cfm-vlan-priority |
Set EOAM CFM CC VLAN priority (PCP).
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 7
|
a10nsp |
Enable A10NSP switch emulation (experimental).
Default: false
|
a10nsp-tx-label |
Transport label used for A10NSP services in dowstream direction.
Default: 0
|
The BNG Blaster supports multiple network interfaces as shown in the example below.
{
"interfaces": {
"network": [
{
"interface": "eth2",
"address": "10.0.0.1/24",
"gateway": "10.0.0.2",
"address-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331::1/64",
"gateway-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331::2"
},
{
"interface": "eth3",
"address": "10.0.1.1/24",
"gateway": "10.0.1.2",
"address-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331:1::1/64",
"gateway-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331:1::2"
}
],
}
}
Using multiple network interfaces requires selecting which network interface
to be used. If not explicitly configured, one of the interfaces is selected
automatically. Therefore, the configuration option network-interface
is supported in different sections.
It is also supported to have multiple VLAN-tagged network interfaces on the same interface link.
VLAN-tagged network interfaces must be referenced by <interface>:<vlan>
in the configuration to distinguish between them.
{
"interfaces": {
"network": [
{
"interface": "eth1",
"address": "10.100.0.2/24",
"gateway": "10.100.0.1",
"vlan": 100
},
{
"interface": "eth1",
"address": "10.200.0.2/24",
"gateway": "10.200.0.1",
"vlan": 200
}
]
},
"streams": [
{
"name": "S100",
"type": "ipv4",
"pps": 10,
"network-interface": "eth1:100",
"destination-ipv4-address": "10.200.0.2"
},
{
"name": "S200",
"type": "ipv4",
"pps": 20,
"network-interface": "eth1:200",
"destination-ipv4-address": "10.100.0.2"
}
]
}
Access Interfaces
The access interfaces are used to emulate PPPoE and IPoE clients.
{ "interfaces": { "access": [] } }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
interface |
Parent interface/link name (e.g. eth0, …).
|
network-interface |
Select the corresponding network interface for those sessions.
Default: first network interface from configuration
|
a10nsp-interface |
Select the corresponding A10NSP interface for those sessions.
Default: first a10nsp interface from configuration
|
type |
Set access type (pppoe or ipoe).
Default: pppoe
|
vlan-mode |
Set VLAN mode to 1:1 or N:1.
Default: 1:1
|
qinq |
Set outer VLAN ethertype to QinQ (0x88a8).
Default: false
|
outer-vlan-min |
Outer VLAN minimum value.
Default: 0 (untagged)
|
outer-vlan-max |
Outer VLAN maximum value.
Default: 0 (untagged)
|
outer-vlan-step |
Outer VLAN step (iterator).
Default: 1
|
outer-vlan |
Set outer-vlan-min/max equally.
|
inner-vlan-min |
Inner VLAN minimum value.
Default: 0 (untagged)
|
inner-vlan-max |
Inner VLAN maximum value.
Default: 0 (untagged)
|
inner-vlan-step |
Inner VLAN step (iterator).
Default: 1
|
inner-vlan |
Set inner-vlan-min/max equally.
|
third-vlan |
Add a static third VLAN (most inner VLAN).
Default: 0 (untagged)
|
ipv4 |
Set false to deactivate IPv4.
|
address |
Static IPv4 base address (IPoE only).
|
address-iter |
Static IPv4 base address iterator (IPoE only).
Default: 0.0.0.0
|
gateway |
Static IPv4 gateway address (IPoE only).
|
gateway-iter |
Static IPv4 gateway address iterator (IPoE only).
Default: 0.0.0.0
|
ipv6 |
Set false to deactivate IPv6.
|
ipv6-link-local |
Static IPv6 link-local address (IPoE only).
|
address-ipv6 |
Static IPv6 address (IPoE only).
|
gateway-ipv6 |
Static IPv6 gateway address (IPoE only).
|
cfm-cc |
Enable EOAM CFM CC.
Default: false
|
cfm-level |
Set EOAM CFM maintenance domain level.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 7
|
cfm-interval |
Set EOAM CFM CCM interval (IEEE 802.1Q encoding).
Values: 3.33ms, 10ms, 100ms, 1s, 10s, 1min, 10min
Default: 1s
|
cfm-md-name |
Set EOAM CFM maintenance domain name (string).
|
cfm-md-name-format |
Set EOAM CFM MD name format.
Default:
NONEValues:
NONE (1) NONEDNS (2) STRINGMAC_INT (3) aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff/123STRING (4) STRING |
cfm-ma-id |
Set EOAM CFM maintenance association identifier.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 65535
|
cfm-ma-name |
Set EOAM CFM maintenance association short name (string).
|
cfm-ma-name-format |
Set EOAM CFM MA name format.
Default:
STRINGValues:
VLAN (1) VLANSTRING (2) STRINGUINT16 (3) NumberVPN_ID (4) 14 hex digits (7 bytes)ICC (32) 13 ASCII chars |
cfm-seq |
Enable EOAM CFM CC sequence numbers.
Default: true
|
cfm-vlan-priority |
Set EOAM CFM CC VLAN priority (PCP).
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 7
|
username |
Overwrite the username from the authentication section.
|
password |
Overwrite the password from the authentication section.
|
authentication-protocol |
Overwrite the username from the authentication section.
|
agent-circuit-id |
Overwrite the agent-circuit-id from the access-line section.
|
agent-remote-id |
Overwrite the agent-remote-id from the access-line section.
|
access-aggregation-circuit-id |
Overwrite the access-aggregation-circuit-id from the
access-line section.
|
rate-up |
Overwrite the rate-up from the access-line section.
|
rate-down |
Overwrite the rate-down from the access-line section.
|
dsl-type |
Overwrite the dsl-type from the access-line section.
|
ppp-mru |
Overwrite PPP MRU (PPPoE only).
|
ipcp |
Overwrite PPP IPCP enable option (PPPoE only).
|
ip6cp |
Overwrite PPP IP6CP enable option (PPPoE only).
|
dhcp |
Overwrite DHCP enable option.
|
dhcp-vendor-class-id |
Overwrite DHCP vendor class id/option 60.
|
dhcpv6 |
Overwrite DHCPv6 enable option.
|
dhcpv6-ldra |
Overwrite DHCPv6 LDRA option.
|
igmp-autostart |
Overwrite IGMP autostart option.
|
igmp-version |
Overwrite IGMP protocol version (1, 2, or 3).
|
access-line-profile-id |
Set access-line-profile identifier.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 65535
|
i1-start |
Iterator {i1} start value.
Default: 1 Range: 0 - 4294967295
|
i1-step |
Iterator {i1} step per session.
Default: 1 Range: 0 - 4294967295
|
i2-start |
Iterator {i2} start value.
Default: 1 Range: 0 - 4294967295
|
i2-step |
Iterator {i2} step per session.
Default: 1 Range: 0 - 4294967295
|
monkey |
Enable monkey testing.
Default: false
|
session-limit |
Limit sessions per access interface.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 10000000
|
session-traffic-autostart |
Overwrite session-traffic autostart.
|
session-group-id |
Set session group identifier.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 65535
|
stream-group-id |
Set stream group identifier.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 65535
|
arp-client-group-id |
Set ARP group identifier.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 65535
|
icmp-client-group-id”, |
Set ICMP group identifier.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 65535
|
http-client-group-id |
Set HTTP group identifier.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 65535
|
tun |
Create a dedicated TUN interface for each session. Use this option
with caution since it can significantly impact scalability.
Default: false
|
For all modes, it is possible to configure between zero and three VLAN
tags on the access interface. The VLAN identifier 0 disables the
corresponding VLAN header.
[ethernet][outer-vlan][inner-vlan][third-vlan][pppoe]...
Untagged
{
"access": {
"interface": "eth1",
"outer-vlan-min": 0,
"outer-vlan-max": 0,
"inner-vlan-min": 0,
"inner-vlan-max": 0
}
}
Single Tagged
{
"access": {
"interface": "eth1",
"outer-vlan-min": 1,
"outer-vlan-max": 4049,
"inner-vlan-min": 0,
"inner-vlan-max": 0
}
}
Double Tagged
{
"access": {
"interface": "eth1",
"outer-vlan-min": 1,
"outer-vlan-max": 4049,
"inner-vlan-min": 7,
"inner-vlan-max": 7
}
}
Triple Tagged
{
"access": {
"interface": "eth1",
"outer-vlan-min": 10,
"outer-vlan-max": 20,
"inner-vlan-min": 128,
"inner-vlan-max": 4000,
"third-vlan": 7
}
}
The BNG Blaster supports also multiple access interfaces or VLAN ranges as shown in the example below.
{
"access": [
{
"interface": "eth1",
"type": "pppoe",
"session-group-id": 1,
"username": "pta@rtbrick.com",
"outer-vlan-min": 1000,
"outer-vlan-max": 1999,
"inner-vlan-min": 7,
"inner-vlan-max": 7
},
{
"interface": "eth1",
"type": "pppoe",
"session-group-id": 2,
"username": "l2tp@rtbrick.com",
"outer-vlan-min": 2000,
"outer-vlan-max": 2999,
"inner-vlan-min": 7,
"inner-vlan-max": 7
},
{
"interface": "eth3",
"type": "pppoe",
"session-group-id": 1,
"username": "test@rtbrick.com",
"outer-vlan-min": 128,
"outer-vlan-max": 4000,
"inner-vlan-min": 7,
"inner-vlan-max": 7
},
{
"interface": "eth4",
"type": "ipoe",
"session-group-id": 3,
"outer-vlan-min": 8,
"outer-vlan-max": 9,
"address": "200.0.0.1",
"address-iter": "0.0.0.4",
"gateway": "200.0.0.2",
"gateway-iter": "0.0.0.4"
}
]
}
The configuration attributes for username, password, agent-remote-id, agent-circuit-id,
and cfm-ma-name/cfm-md-name support variable substitution. The variable {session-global} will
be replaced with the actual session-id starting from 1 and incremented for every
new session. The variable {session} is incremented per-interface section. The
variables {outer-vlan} and {inner-vlan} will be replaced with the corresponding
VLAN identifier or 0 if not defined. The two variables {i1} and {i2} are
configurable per-interface sections with user-defined start values and steps.
The BNG Blaster supports the VLAN mode 1:1 (default) and N:1. The first one
assigns a dedicated VLAN per subscriber. The VLAN mode N:1 assigns one VLAN to N
subscribers and therefore only one VLAN combination is supported per access interface
section using this mode.
{
"access": [
{
"interface": "eth1",
"type": "pppoe",
"vlan-mode": "N:1",
"username": "test@rtbrick.com",
"outer-vlan": 7
},
{
"interface": "eth2",
"type": "pppoe",
"vlan-mode": "N:1",
"username": "test@rtbrick.com",
"outer-vlan": 2000,
"inner-vlan": 7,
},
]
}
One or more access interface blocks can be grouped using the session-group-id,
which allows applying some commands like session-start, session-stop or
session-restart to all sessions belonging to the same group. The example
below shows how to assign all even VLAN identifiers to session group 1 and
all odd VLAN identifiers to session group 2.
{
"access": [
{
"interface": "eth1",
"type": "pppoe",
"session-group-id": 1,
"username": "even@rtbrick.com",
"outer-vlan-min": 1000,
"outer-vlan-max": 1998,
"outer-vlan-step": 2,
"inner-vlan": 7
},
{
"interface": "eth1",
"type": "pppoe",
"session-group-id": 2,
"username": "odd@rtbrick.com",
"outer-vlan-min": 1001,
"outer-vlan-max": 1999,
"outer-vlan-step": 2,
"inner-vlan": 7
},
]
}
The BNG Blaster supports access and network interface functions on the same interface link if both are tagged with disjoint VLAN ranges.
A10NSP Interfaces
The A10NSP interface function is required for L2BSA tests and emulates a layer two provider interface. The term A10 refers to the end-to-end ADSL network reference model from TR-025.
{ "interfaces": { "a10nsp": [] } }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
interface |
Parent interface/link name (e.g. eth0, …).
|
qinq |
Set outer VLAN ethertype to QinQ (0x88a8).
Default: false
|
mac |
Optional set gateway interface address manually.
Default: parent interface/link MAC address
|
The BNG Blaster supports multiple A10NSP interfaces as shown in the example below.
{
"interfaces": {
"a10nsp": [
{
"interface": "eth4",
"qinq": true,
"mac": "02:00:00:ff:ff:01"
},
{
"interface": "eth5",
"qinq": false,
"mac": "02:00:00:ff:ff:02"
}
],
}
}
Note
The A10NSP interface function can’t reside on the same link with with network or access interface functions!
I/O Modes
The BNG Blaster supports many configurable I/O modes listed with bngblaster -v.
In the default mode packet_mmap_raw, all packets are received in a Packet MMAP
ring buffer and sent through RAW packet sockets.
$ bngblaster -v
Version: 0.8.1
Compiler: GNU (7.5.0)
IO Modes: packet_mmap_raw (default), packet_mmap, raw
Packet MMAP
Packet MMAP is a so-called PACKET_RX_RING/PACKET_TX_RING abstraction where a user-space program gets a fast lane into reading and writing to kernel interfaces using a shared ring buffer. The shared ring buffer is a memory-mapped window shared between the kernel and the user space. This low overhead abstraction allows us to transmit and receive traffic without doing expensive system calls. Sending and transmitting traffic via Packet MMAP is as easy as copying a packet into a buffer and setting a flag.
Using I/O mode packet_mmap_raw or packet_mmap limits the maximum
stream packet length to 3936 bytes on most systems. The actual limit is dynamically
calcualted based on pagesize (typically 4096) minus overhead.
RAW
RAW Packet Sockets. are used to receive or send raw packets at the device driver (OSI layer 2) level.
The I/O mode raw allows steam packet lengths of up to 9000 bytes (layer 3).
DPDK
DPDK support should be considered as experimental. This I/O mode is detailed explained in the DPDK section of the performance guide.