ISIS
Intermediate System to Intermediate System (ISIS, also written IS-IS) is a routing protocol designed to move information efficiently within a network.
The ISIS protocol is defined in ISO/IEC 10589:2002 as an international standard within the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference design. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) republished ISIS in RFC 1142, but that RFC was later marked as historic by RFC 7142 because it republished a draft rather than a final version of the ISO standard, causing confusion.
ISIS has been called the de facto standard for a large service provider network backbones.
The BNG Blaster can emulate multiple ISIS instances. An ISIS instance
is a virtual ISIS node with one or more network interfaces attached. Such a
node behaves like a “real router” including database synchronization and
flooding. Every instance generates a self originated LSP describing the
node itself.
Configuration
Following an example ISIS configuration with one instance attached to two network interfaces.
{
"interfaces": {
"network": [
{
"interface": "eth1",
"address": "10.0.1.2/24",
"gateway": "10.0.1.1",
"address-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331:1::2/64",
"gateway-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331:1::1",
"isis-instance-id": 1,
"isis-level": 1,
"isis-l1-metric": 100,
},
{
"interface": "eth2",
"address": "10.0.2.2/24",
"gateway": "10.0.2.1",
"address-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331:2::2/64",
"gateway-ipv6": "fc66:1337:7331:2::1",
"isis-instance-id": 1
}
]
},
"isis": [
{
"instance-id": 1,
"system-id": "1921.6800.1001",
"router-id": "192.168.1.1",
"hostname": "R1",
"area": [
"49.0001/24",
"49.0002/24"
],
"hello-padding": true,
"lsp-lifetime": 65535,
"level1-auth-key": "secret",
"level1-auth-type": "md5",
"sr-base": 2000,
"sr-range": 3600
}
]
}
{ "isis": {} }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
instance-id |
ISIS instance identifier.
|
level |
Level.
Default: 3 Range: 1 - 3
|
protocol-ipv4 |
Enable/disable IPv4 routing.
Default: true
|
protocol-ipv6 |
Enable/disable IPv6 routing.
Default: true
|
level1-auth-key |
Level 1 authentication key.
|
level1-auth-type |
Level 1 authentication type (simple or md5).
|
level1-auth-hello |
Level 1 hello authentication.
|
level1-auth-csnp |
Level 1 CSNP authentication.
|
level1-auth-psnp |
Level 1 PSNP authentication.
|
level2-auth-key |
Level 2 authentication key.
|
level2-auth-type |
Level 2 authentication type (simple or md5).
|
level2-auth-hello |
Level 2 hello authentication.
|
level2-auth-csnp |
Level 2 CSNP authentication.
|
level2-auth-psnp |
Level 2 PSNP authentication.
|
hello-interval |
Hello interval in seconds.
Default: 10 Range: 1 - 65535
|
hello-padding |
Enable/disable hello padding.
Default: false
|
hold-time |
ISIS hold time in seconds.
Default: 30 Range: 1 - 65535
|
lsp-buffer-size |
ISIS LSPBufferSize in bytes.
Default: 1492 Range: 128 - 9192
|
lsp-lifetime |
ISIS LSP lifetime in seconds.
Default: 65535 Range: 330 - 65535
|
lsp-refresh-interval |
ISIS LSP refresh interval in seconds.
Default: 300 Range: 1 - 65535
|
lsp-retry-interval |
ISIS LSP retry interval in seconds.
Default: 5 Range: 1 - 65535
|
lsp-tx-interval |
ISIS LSP TX interval in ms (time between LSP send windows).
Default: 10 Range: 1 - 65535
|
lsp-tx-window-size |
ISIS LSP TX window size (LSP send per window).
Default: 1 Range: 1 - 65535
|
csnp-interval |
ISIS CSNP interval in seconds.
Default: 30 Range: 1 - 65535
|
hostname |
ISIS hostname.
Default: bngblaster
|
router-id |
ISIS router identifier.
Default: 10.10.10.10
|
system-id |
ISIS system identifier.
Default: 0100.1001.0010
|
area |
ISIS area(s).
Default: 49.0001/24
|
sr-algo |
ISIS SR algorithm(s), multiple possible.
Default: disabled Range: 0 - 255
|
sr-base |
ISIS SR base.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 1048575
|
sr-range |
ISIS SR range.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 1048575
|
sr-node-sid |
ISIS SR node SID.
Default: 0 Range: 0 - 1048575
|
adjacency-sid-base |
Enable Adjacency SID generation.
Default: disabled Range 256 - 4096
|
teardown-time |
ISIS teardown time in seconds.
Default: 5 Range: 0 - 65535
|
The support for multiple instances allows different use cases. One example might be to create two instances connected to the device or network under test. Now inject an LSP on one instance and check if learned over the tested network on the other instance.
Every ISIS instance can be also connected to an emulated link state graph loaded by MRT files as shown in the example below.
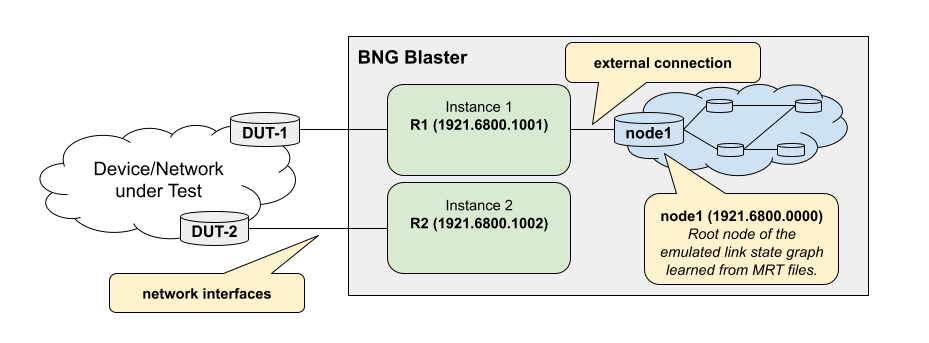
{
"isis": [
{
"instance-id": 1,
"system-id": "1921.6800.1001",
"router-id": "192.168.1.1",
"hostname": "R1",
"external": {
"mrt-file": "isis.mrt",
"connections": [
{
"system-id": "1921.6800.0000.00",
"l1-metric": 1000,
"l2-metric": 2000
}
]
}
},
{
"instance-id": 2,
"system-id": "1921.6800.1002",
"router-id": "192.168.1.2",
"hostname": "R2"
}
]
}
{ "isis": { "external": {} } }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
purge |
Automatically purge all external LSP during teardown. This option
requires a reasonable teardown-time depending on the database size.
Default: true
|
auto-refresh |
Automatically refresh all external LSP.
Default: false
|
mrt-file |
MRT file
|
The node N1 in this example also needs to advertise the
reachability to node B1.
{ "isis": { "external": { "connections": [] } } }
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
system-id |
ISIS system identifier.
|
l1-metric |
ISIS level 1 interface metric.
Default: 10
|
l2-metric |
ISIS level 2 interface metric.
Default: 10
|
Adjacencies
The BNG Blaster supports broadcast and P2P (default) adjacencies with 3-way-handshake only.
$ sudo bngblaster-cli run.sock isis-adjacencies
{
"status": "ok",
"code": 200,
"isis-adjacencies": [
{
"interface": "eth1",
"type": "P2P",
"level": "L1",
"instance-id": 2,
"adjacency-state": "Up",
"peer": {
"system-id": "0100.1001.0022"
}
},
{
"interface": "eth2",
"type": "P2P",
"level": "L1",
"instance-id": 1,
"adjacency-state": "Up",
"peer": {
"system-id": "0100.1001.0021"
}
}
]
}
Database
The BNG Blaster distinguishes between three different source types of LSP entries in the ISIS database.
The type self is used for the self-originated LSP describing the own
BNG Blaster ISIS instance. LSP entries of type adjacency are learned
via ISIS adjacencies. The type external is used for those LSP entries
learned via MRT files or injected via isis-lsp-update command.
$ sudo bngblaster-cli run.sock isis-database instance 1 level 1
{
"status": "ok",
"code": 200,
"isis-database": [
{
"id": "0000.0000.0001.00-00",
"seq": 1,
"lifetime": 65535,
"lifetime-remaining": 65529,
"source-type": "external"
},
{
"id": "0100.1001.0011.00-00",
"seq": 2,
"lifetime": 65535,
"lifetime-remaining": 65507,
"source-type": "self"
},
{
"id": "0100.1001.0021.00-00",
"seq": 2,
"lifetime": 65524,
"lifetime-remaining": 65506,
"source-type": "adjacency",
"source-system-id": "0100.1001.0021"
},
{
"id": "0100.1001.0022.00-00",
"seq": 2,
"lifetime": 65524,
"lifetime-remaining": 65506,
"source-type": "adjacency",
"source-system-id": "0100.1001.0021"
}
]
}
The BNG Blaster automatically purges all LSPs of type
self and external during teardown. This is done by
generating LSPs with newer sequence numbers and a lifetime
of 30 seconds only. This lifetime is enough to flood the purge
LSP over the whole network under test.
Flooding
The BNG Blaster floods LSPs received to all other active adjacencies of the ISIS instance except to those with peer system-id equal to the source system-id of the LSP.
Limitations
Currently there is no support for route leaking between levels.
LSP Update Command
It is also possible to inject external LSPs using the isis-lsp-update
command.
The command expects a list of hex encoded PDU’s including
the ISIS common header starting with 0x83.
$ cat command.json | jq .
{
"command": "isis-lsp-update",
"arguments": {
"instance": 1,
"pdu": [
"831b0100120100000021ffff010203040506000000000003c0d103010403490001",
"831b0100120100000021ffff010203040506000100000003bad603010403490001"
]
}
}
LSP Update via Scapy
The following example shows how to generate LSPs via Scapy
and inject them using the isis-lsp-update command.
import sys
import socket
import os
import json
from scapy.contrib.isis import *
def error(*args, **kwargs):
"""print error and exit"""
print(*args, file=sys.stderr, **kwargs)
sys.exit(1)
def execute_command(socket_path, request):
if os.path.exists(socket_path):
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_UNIX, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
client.connect(socket_path)
client.send(json.dumps(request).encode('utf-8'))
data = ""
while True:
junk = client.recv(1024)
if junk:
data += junk.decode('utf-8')
else:
break
print(json.dumps(json.loads(data), indent=4))
except Exception as e:
error(e)
finally:
client.close()
else:
error("socket %s not found" % socket_path)
def main():
"""main function"""
socket_path = sys.argv[1]
command = {
"command": "isis-lsp-update",
"arguments": {
"instance": 1,
"pdu": []
}
}
tlvs = ISIS_AreaTlv(areas=ISIS_AreaEntry(areaid='49.0001'))
pdu = ISIS_CommonHdr()/ISIS_L1_LSP(lifetime=65535, lspid='0102.0304.0506.00-00', seqnum=3, tlvs=tlvs)
command["arguments"]["pdu"].append(pdu.build().hex())
pdu = ISIS_CommonHdr()/ISIS_L1_LSP(lifetime=65535, lspid='0102.0304.0506.00-01', seqnum=3, tlvs=tlvs)
command["arguments"]["pdu"].append(pdu.build().hex())
execute_command(socket_path, command)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
MRT Files
The BNG Blaster can load LSPs from a MRT file as defined in RFC6396.
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Timestamp |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Type | Subtype |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Length |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Message... (variable)
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
The message field contains the complete ISIS LSP PDU including
the ISIS common header starting with 0x83.
Those files can be loaded at startup via the configuration option
"isis": { "external": { "mrt-file": "<file>" } } or alternative
via isis-load-mrt command.
$ sudo bngblaster-cli run.sock isis-load-mrt file test.mrt instance 1
LSPGEN
The BNG Blaster includes a tool called lspgen, which is able to generate
topologies and link state packets for export as MRT and PCAP files. This tool
is also able to inject LSAs directly using the isis-lsp-update
command.